1/23
Health Sciences
Penn Study Finds Moderate Sedation More Effective than General Anesthesia for TAVR Patients
A new study finds the use of moderate sedation, in which patients do not need a breathing tube, leads to better clinical outcomes as compared to general anesthesia for patients undergoing transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Penn Medicine Researcher Receives $3 million NCI Grant to Study Links between Liver Cancer and HIV
Vincent Lo Re, MD, MSCE, an assistant professor of Medicine in the division of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, has been awarded a $3 million grant from the National
Penn Researcher Calls for Changes to Increase Access to Life-Saving Colorectal Cancer Screening
Colorectal cancer is the second highest cause of cancer death in the United States, expected to claim the lives of an estimated 49,190 people in 2016.
Three Penn Students Named HHMI Medical Research Fellows
Three graduate students from the University of Pennsylvania have been selected as Medical Research Fellows by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI).
Testing Non-Breast/Ovarian Cancer Genes in High-Risk Women Leaves More Questions than Answers, Penn Study Finds
Running large, multi-gene sequencing panels to assess cancer risk is a growing trend in medicine as the price of the technology declines and more precise approaches to cancer care gain steam. The tests are particularly common among breast and ovarian cancer patients.
Three Penn Students Named HHMI Medical Research Fellows
Three graduate students from the University of Pennsylvania have been selected as Medical Research Fellows by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
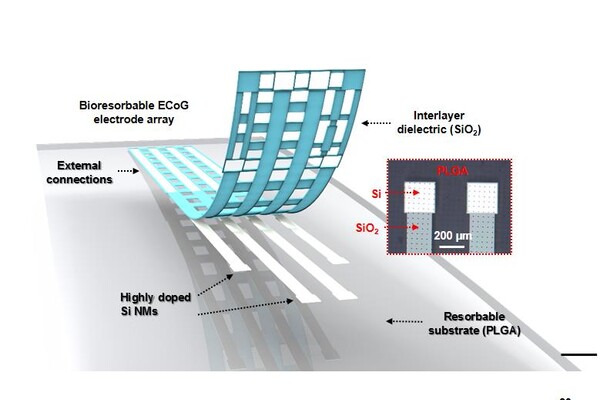
Penn Medicine: Proof-of-Concept Animal Study Shows that Flexible, Dissolvable Silicon Electronic Device Holds Promise for Brain Monitoring
An implantable brain device that literally melts away at a pre-determined rate minimizes injury to tissue normally associated with standard electrode implantation, according to research led by a team from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
Good Nutrition Positively Affects Social Development, Penn Research Shows
Proper nutrition during childhood can positively affect a child’s social behaviors and development.
Four Penn Medicine Physicians Elected to Prestigious American Society for Clinical Investigation
Four Penn Medicine physicians were elected this year to the American Society for Clinical Investigation (ASCI), an honor society of more than 3,000 interdisciplinary physician-scientists from across the nation. Ronny I.
Penn Study Points to Path for Antibiotic-free Treatment for Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, or AD, a chronic inflammatory skin condition and the most common form of eczema, is estimated to afflict as much as 10 percent of the population in the United States, and it is much more common now than it was 50 years ago. Veterinary clinical estimates also show that approximately 10 percent of dogs have atopic dermatitis.
In the News
Bird flu suspected in deaths of 200 snow geese in Pennsylvania’s Lehigh Valley
Stephen Cole of the School of Veterinary Medicine says that indoor cats are contracting bird flu through raw pet foods of poultry origin or raw milk products.
FULL STORY →
The surgeon general calls for new warning labels on alcohol—here’s the truth about how it impacts your health
Henry Kranzler of the Perelman School of Medicine says that alcohol’s effects on the brain are observed more readily because it’s the organ of behavior.
FULL STORY →
Tuberculosis rates plunge when families living in poverty get a monthly cash payout
Aaron Richterman of the Perelman School of Medicine says that there are large and underappreciated benefits of cash-transfer programs, such as potentially ending a tuberculosis epidemic.
FULL STORY →
Scientists are racing to develop a new bird flu vaccine
Drew Weissman and Scott Hensley of the Perelman School of Medicine are testing a vaccine to prevent a strain of H5N1 bird flu in chickens and cattle.
FULL STORY →
Cancer breakthrough as ‘speckles’ may reveal best treatment
A paper co-authored by PIK Professor Shelley Berger finds that patterns of “speckles” in the heart of tumor cells could help predict how patients with a common form of kidney cancer will respond to treatment options.
FULL STORY →