
nocred
Imagine the brain as an air traffic control tower, overseeing the crucial and complex operations of the body’s ‘airport.’ This tower, essential for coordinating the ceaseless flow of neurological signals, is guarded by a formidable layer that functions like the airport’s security team, diligently screening everything and everyone, ensuring no unwanted intruders disrupt the vital workings inside.
However, this security, while vital, comes with a significant drawback: sometimes, a ‘mechanic’—in the form of critical medication needed for treating neurological disorders—is needed inside the control tower to fix arising issues. But if the security is too stringent, denying even these essential agents entry, the very operations they’re meant to protect could be jeopardized.
Now, researchers led by Michael Mitchell of the University of Pennsylvania are broaching this long-standing boundary in biology, known as the blood-brain barrier, by developing a method akin to providing this mechanic with a special keycard to bypass security. Their findings, published in the journal Nano Letters, present a model that uses lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) to deliver mRNA, offering new hope for treating conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and seizures—not unlike fixing the control tower’s glitches without compromising its security.
“Our model performed better at crossing the blood-brain barrier than others and helped us identify organ-specific particles that we later validated in future models,” says Mitchell, associate professor of bioengineering at Penn’s School of Engineering and Applied Science, and senior author on the study. “It’s an exciting proof of concept that will no doubt inform novel approaches to treating conditions like traumatic brain injury, stroke, and Alzheimer’s.”
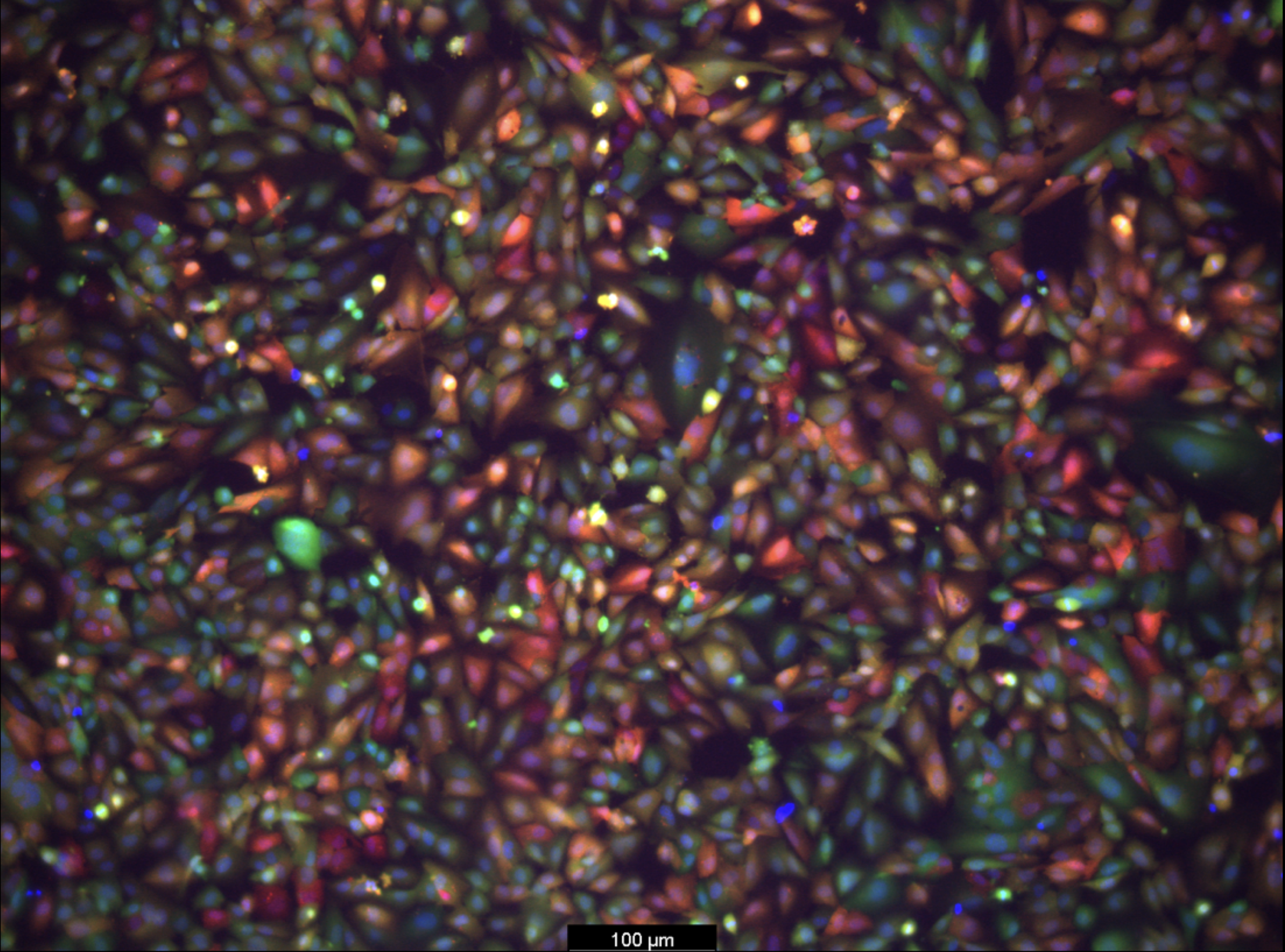
To develop the model, Emily Han, a Ph.D. candidate and NSF Graduate Research Fellow in the Mitchell Lab and first author of the paper, explains that it started with a search for the right in vitro screening platform, saying, “I was combing through the literature, most of the platforms I found were limited to a regular 96-well plate, a two-dimensional array that can’t represent both the upper and lower parts of the blood-brain barrier, which correspond to the blood and brain, respectively.”
Han then explored high-throughput transwell systems with both compartments but found they didn’t account for mRNA transfection of the cells, revealing a gap in the development process. This led her to create a platform capable of measuring mRNA transport from the blood compartment to the brain, as well as transfection of various brain cell types including endothelial cells and neurons.
“I spent months figuring out the optimal conditions for this new in vitro system, including which cell growth conditions and fluorescent reporters to use,” Han explains. “Once robust, we screened our library of LNPs and tested them on animal models. Seeing the brains express protein as a result of the mRNA we delivered was thrilling and confirmed we were on the right track.”
The team’s platform is poised to significantly advance treatments for neurological disorders. It’s currently tailored for testing a range of LNPs with brain-targeted peptides, antibodies, and various lipid compositions. However, it could also deliver other therapeutic agents like siRNA, DNA, proteins, or small molecule drugs directly to the brain after intravenous administration.
What’s more, this approach isn’t limited to the blood-brain barrier as it shows promise for exploring treatments for pregnancy-related diseases by targeting the blood-placental barrier, and for retinal diseases focusing on the blood-retinal barrier.
The team is eager to use this platform to screen new designs and test their effectiveness in different animal models. They are particularly interested in working with collaborators with advanced animal models of neurological disorders.
“We’re collaborating with researchers at Penn to establish brain disease models,” Han says. “We’re examining how these LNPs impact mice with various brain conditions, ranging from glioblastoma to traumatic brain injuries. We hope to make inroads towards repairing the blood-brain barrier or target neurons damaged post-injury.”
Michael Mitchell is an associate professor in the Department of Bioengineering in the School of Engineering and Applied Science and the director of the Lipid Nanoparticle Synthesis Core at the Penn Institute for RNA Innovation at the University of Pennsylvania.
Emily Han is a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Engineering and Applied Science at Penn.
Other authors include Marshall Padilla, Rohan Palanki, Dongyoon Kim, Kaitlin Mrksich, Jacqueline Li, Sophia Tang, and Il-Chul Yoon of Penn Engineering.
This research was supported by the National Institute of Health (Award DP2 TR002776, Grant No. T90DE030854 and F30HL162465−01A1); a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Career Award at the Scientific Interface; and the National Science Foundation (Award CBET-2145491 and 1845298).

nocred

nocred

Despite the commonality of water and ice, says Penn physicist Robert Carpick, their physical properties are remarkably unique.
(Image: mustafahacalaki via Getty Images)

Organizations like Penn’s Netter Center for Community Partnerships foster collaborations between Penn and public schools in the West Philadelphia community.
nocred